PlasmaWave technology is a bipolar ionization process developed by Winix to boost the air cleaning capabilities of their air purifiers, while generating minimal levels of potentially harmful chemical byproducts like ozone.
But is this something you should be worried about?
The reason I ask is that most people become concerned about ozone generation upon reading the words ‘ionizer’ or ‘ionization’.
It is a valid concern, especially considering there have been a number of high-profile class action lawsuits involving ionizer air purifier models releasing ozone into the air to help remove pollutants. These lawsuits have led to very public bankruptcies of air purifier companies and even a blanket recommendation from Consumer Reports in 2003 to avoid ionizers altogether.
By 2010, all portable air purifiers sold in California had to be certified by the California Air Resources Board after being tested for ozone emissions to ensure devices meet the ozone emission concentration limit of 0.050 parts per million (50 ppb).
All these events led to big changes in the way in which air purifier manufacturers design these devices.
The original ionizer air purifiers used high voltage to release negative oxygen ions that would attach themselves to mid-sized particles, forcing them to fall onto surfaces. The problem was that this process also produced high levels of ozone and could lead to other potentially dangerous chemical byproducts.
Enter PlasmaWave.
How is PlasmaWave different from old-fashioned ionizers?
The team at Winix developed a new approach to ionization, with chemical by-products in mind—the result was PlasmaWave.

Winix designed a new type of low-voltage ionization process that help reduce air pollutants, while producing much lower levels of ozone.
PlasmaWave releases electrical discharges that alter the molecules in the air to create positive hydrogen and negative oxygen ions (a.k.a. hydroxyl radicals). These hydroxyl radicals attach themselves to air pollutants to break down their chemistry but they are considered safer than ozone as they have a much shorter life.
To be clear, when enabling PlasmaWave, the air purifier will still produce ozone as a byproduct—but it’s a very low concentration that is well below the 50 ppb limit established by CARB.
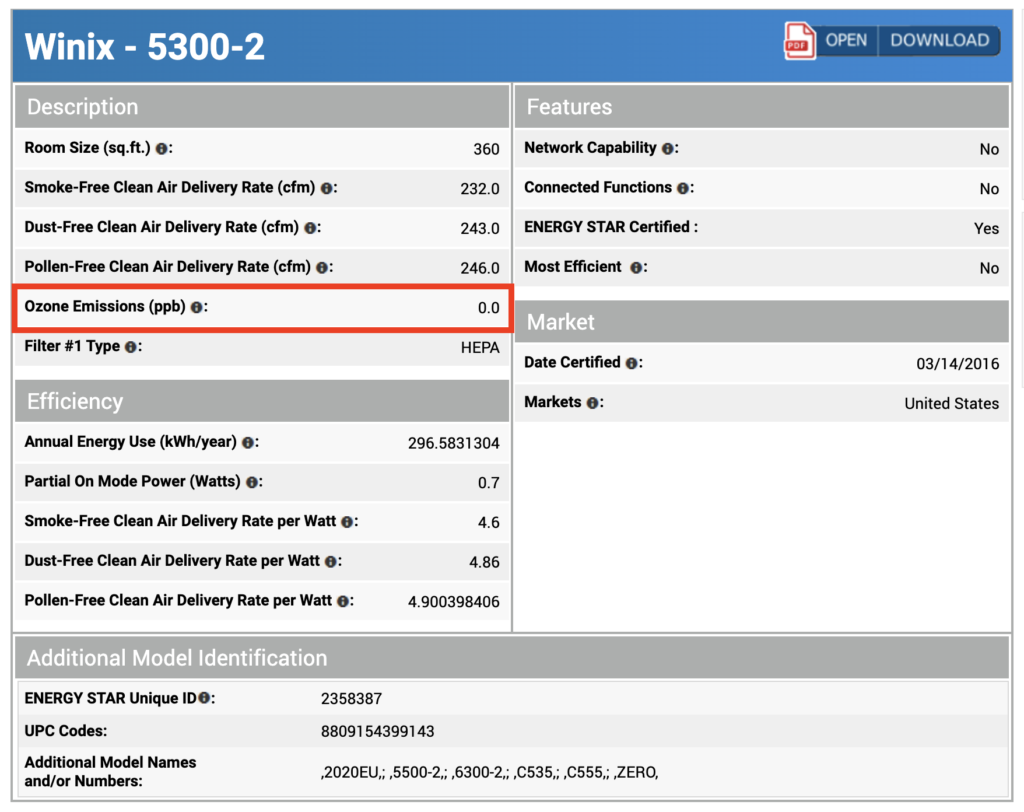
For example, the EnergyStar report for the Winix 5500-2 shows zero ozone production, as any ozone is likely removed by the activated carbon filter in the air purifier before the air leaves the machine.
Another air purifier that has been certified as ozone-free even though it uses ionization technology is the Blueair 211+ (check out the Intertek certificate)—Blueair has trademarked their ionization process under HEPASilent technology.
But real life is not reflected in lab tests and those who have a sensitivity to ozone might disagree with the 50 ppb limits. Plus, older and broken devices may, over time, release higher levels of ozone.
If you do go down the route of using a bipolar ionization-powered air purifier, then be sure only to choose air purifier models that meet UL 2998 standard certification for Zero Ozone Emissions from Air Cleaners.
My tip is to look for models that will allow you to enable and disable the ionizer function, as is the case with Winix devices. I hear from consumers who only realized they are sensitive to the chemicals produced by ionization technologies after buying devices without an on/off button.
That’s why we don’t recommend devices that don’t allow you to disable the ionizer function, as we see with Blueair Blue Pure models.
How effective is Plasmawave?
Our data shows that this Winix technology leads to an improvement in particle removal performance.

We don’t test for VOC removal performance yet, so we don’t have any firsthand data on how effective PlasmaWave can be at dealing with unwanted smells and gases. We have read a 2022 study into the effectiveness of ionizer technology (not PlasmaWave specifically) that showed mixed reports, as researchers found a reduction of some VOC levels while recording an increase in others.
The good news is that we have collected firsthand data on the particle removal performance of PlasmaWave-enabled air purifiers.
We used our PurpleAir Zen sensor to record how long it took for each of the following Winix air purifiers to clear the air of all PM1 incense smoke particles inside our 728 cubic feet test room:
| With PlasmaWave | Without PlasmaWave | % Improvement in Particle Removal CADR | |
| Winix 5500-2 | 259 cfm | 248 cfm | 4.33% |
| Winix 5510 | 248 cfm | 229 cfm | 7.94% |
| Winix T810 | 229 cfm | 229 cfm | 0% |
The CADR figures above are based on our own testing. We compared PM1 removal rates achieved by each device with and without PlasmaWave enabled against the natural ventilation rate of our 728 cubic feet test room using the Air Cleaner Efficacy Investigation tool (ACE IT).
As you can see from the table, our data shows that PlasmaWave generally helps remove small particles quicker when combined with the True HEPA particle filter used in the Winix devices, leading to a small increase in overall CADR of around 5% on average.
This small improvement matched up with another study from the Built Environment Research Group at the Illinois Institute of Technology, which showed a 5% improvement in air cleaning performance for dust particles (0.5-3 µm) when PlasmaWave was enabled versus not.
However, if you are sensitive to ozone or other VOCs, you may want to avoid any type of ionizer. If that’s you, make sure to check out our list of the best-performing air purifiers that produce zero ozone.
Modern mechanical-powered air filters are much better than in previous years, so high CADR can still be achieved without any bipolar ionization process.
If you have more questions about PlasmaWave or ionizers in general, please leave them in the comments below, and I will do my best to answer them.





