The air we breathe is one of the most essential factors in our well-being.
Humans take about 22,000 breaths daily, inhaling life-sustaining oxygen while taking in harmful pollutants from natural and man-made sources.
While most pollutants are invisible to the naked eye, their impacts on human health are well-documented. In several studies, a decrease of 10 micrograms per cubic meter of particulate matter was associated with an increase of approximately one year in life expectancy.
Because the county with the worst air quality in the United States has about 18 more micrograms of particulate matter per cubic meter than the county with the cleanest air, where you live in the United States can significantly impact your health.
There are over 2,000 ambient outdoor air monitors throughout the United States. These monitors measure the concentrations of some of the most harmful pollutants, including inhalable particulate matter, toxic gases and ozone.
To determine the states with the worst air quality, we ranked states based on the Air Quality Index (AQI), a composite index on a scale of 0 to 500 consisting of six factors:
1️⃣ Ambient particulate matter (PM10)
2️⃣ Fine particulate matter (PM2.5)
3️⃣ Ozone (O3)
4️⃣ Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
5️⃣ Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
6️⃣ Carbon monoxide (CO)
Using data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, we aggregated the latest data on annual AQI from the county to the state level. For city data, we crosswalked county-level data with county seat assignments.
Key findings
- Arizona is the state with the worst air quality on average. The nation-leading AQI of 48.8 is mainly due to air pollution in Phoenix, the largest city in the state, which spent a third of last year under conditions deemed by the EPA as unhealthy.
- The state with the best air quality is Alaska, with an AQI of just 17.3.
- Hawaii is the state that has the worst sulfur dioxide pollution of any state by far — primarily due to the presence of active volcanoes on the archipelago.
- All 20 cities with the worst air quality overall are in the Sun Belt states of Arizona, California, New Mexico and Texas, where extreme heat and rapid urbanization create a vicious cycle of air pollution.
- The city with the best air quality is Chatham, Virginia.
Arizona has the worst air in the United States, followed by California
Our map of the best and worst states for air quality shows the myriad sources and trends of harmful air pollutants. In the western states of Arizona, California and Utah, for example, poor air quality is primarily the result of rapid urbanization and unique climate factors that exacerbate air pollution issues.
Massive dust storms can generate particulate matter in an arid state like Arizona. Meanwhile, in California, recurring wildfires release vast amounts of smoke and pollutants that get trapped in the atmosphere.
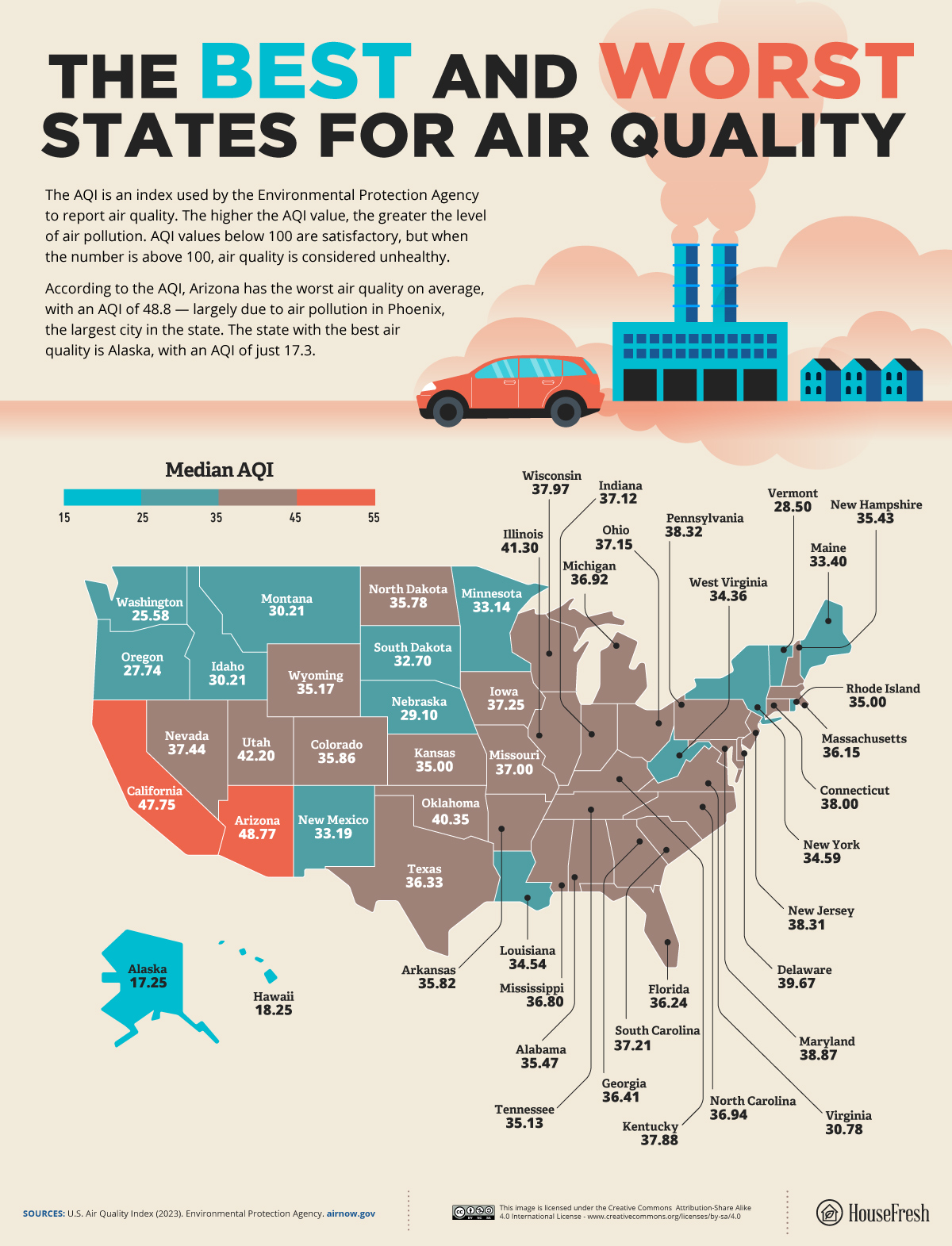
Other states that rank among the worst in air quality include states with histories of industrialization and heavy manufacturing, such as Illinois, Pennsylvania and New Jersey. While air pollution overall has fallen significantly since the Clean Air Act of 1970, the legacy of factories, power plants and other industrial facilities in these states continues to impact the health of their populations.
Top 5 worst U.S. states for air quality
#1. Arizona (Median AQI: 48.77)
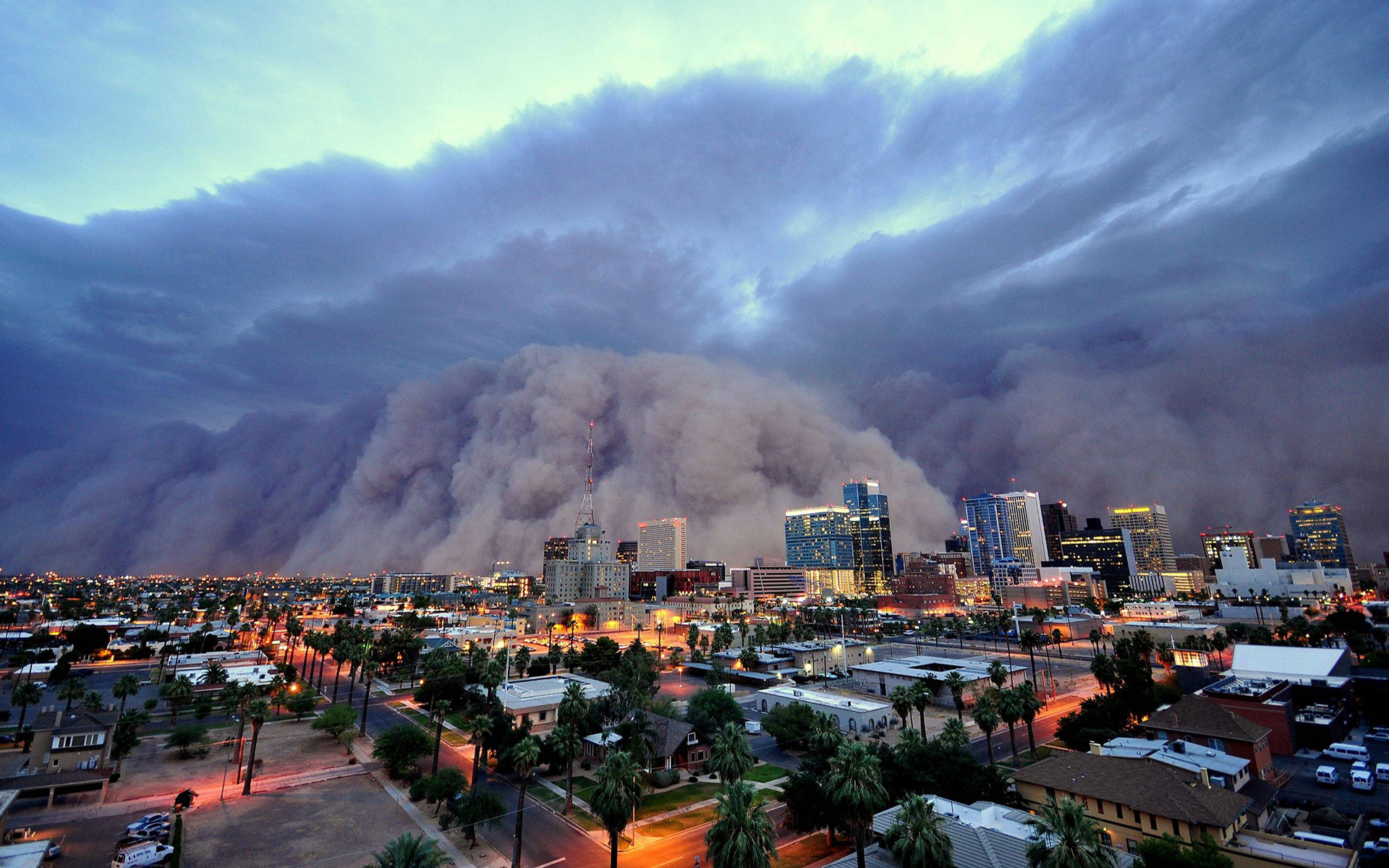

Image Source: Wikimedia
The arid regions of Arizona are well known for their sudden dust storms on windy days. A dust storm occurs when a large mass of cold, unstable air rushes across dry ground that’s covered with loose silt and fine sand — whipping up a storm. They can be dangerous (and scary) if you find yourself stuck in one.
Known as haboobs, the dust storms in Arizona tend to be more severe than in other areas. Arizona’s most intense dust storms occur during the summer — because of strong downdrafts generated by intense monsoonal thunderstorm activity.
When visibility is impaired, and things look very dusty, your best bet is to avoid the outdoors and seek shelter immediately.
If you’re in an area where dust is an issue, check out our selection of the best air purifiers for dust.
#2. California (Median AQI: 47.75)
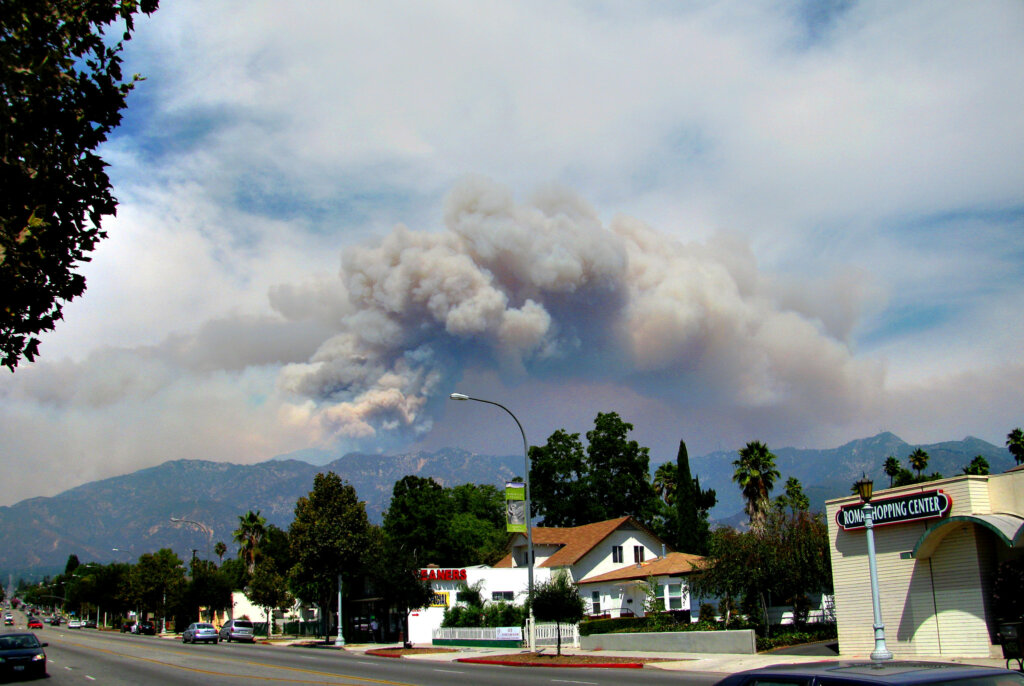

Image Source: EricF2000, Flickr
California has a history of severe wildfires due to its dry weather and hot summers. But the state has experienced some of the most devastating wildfire seasons on record in recent years. According to CARB, about 25 million acres —a quarter of California’s land— are currently at very high or extreme fire risk.
These massive wildfires produce dense and hazardous smoke that can contaminate the air for months or even years. The smoke can travel extensive distances, reaching urban areas that are far removed from the actual fire sources.
Poor air quality can reach dangerous levels during wildfire season. The best way to tackle it is by minimizing exposure and simply staying home with shut doors and windows.
#3. Utah (Median AQI: 42.20)
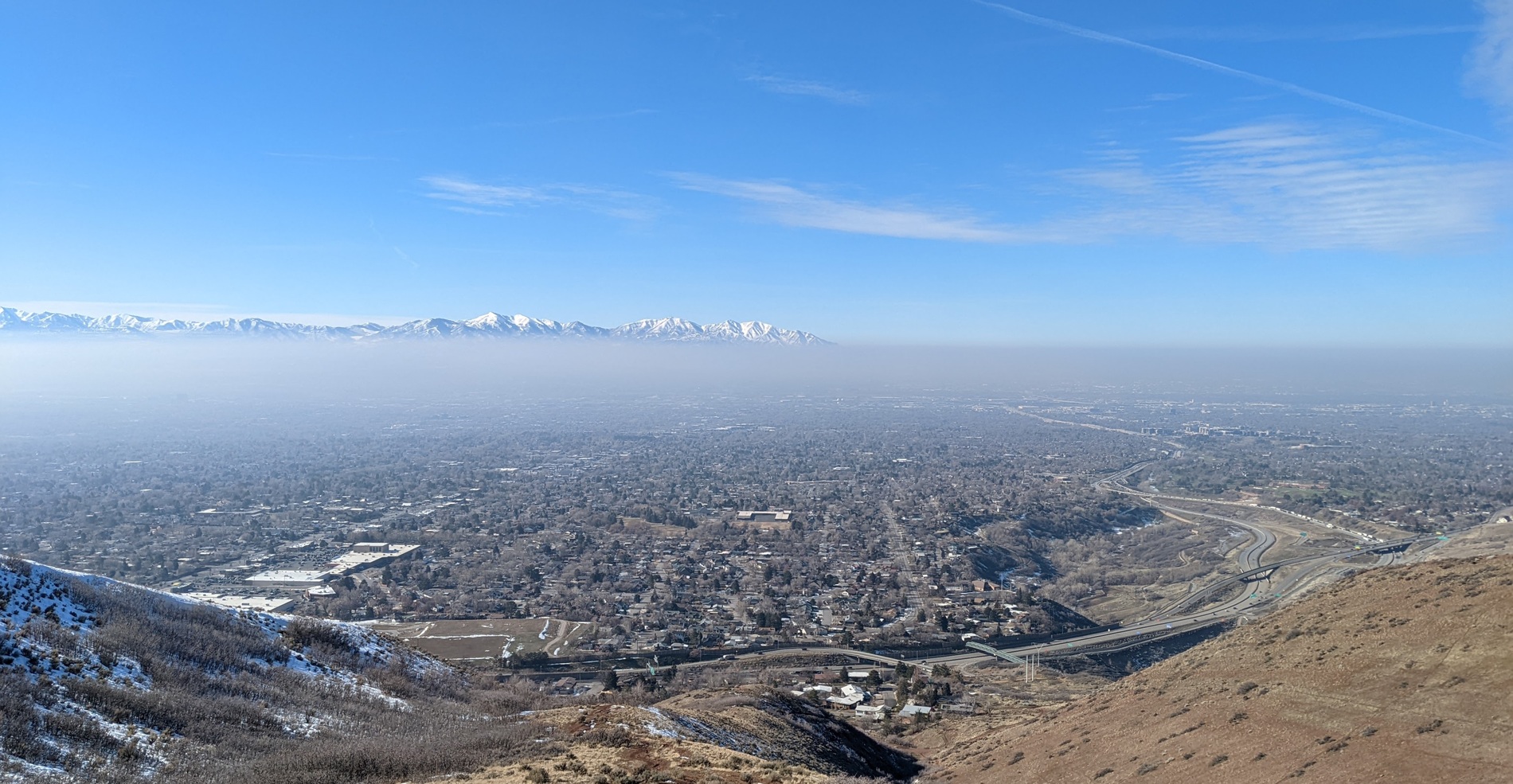

Image Source: Wikimedia
Utah’s typically clear skies during winter can transform into a hazy and smoggy spectacle. The foggy skies are usually the product of an atmospheric phenomenon known as inversion, in which common pollutants, otherwise not so visible, build up in the air up to unhealthy levels.
Inversions happen when the cold air near the surface gets trapped beneath a layer of warmer air above. Following a snowstorm, the calm winds reduce the natural mixing of cold and warm air, while the combination of clear skies and long nights allows the ground to cool over an extended period. As a result, the surface temperature drops further and the temperature difference becomes more pronounced.
- During inversions, try to stay indoors as much as possible and avoid unnecessary exposure to the polluted air.
- Keep your indoor air clean and avoid wood-burning stoves or heaters.
- For those relying on wood for heat, The UDEQ has the Wood Stove and Fireplace Conversion Assistance Program to help replace wood stoves or fireplaces with natural gas, propane-fueled, or electric appliances.
Visit our best air purifiers list to improve indoor air quality during inversions.
#4. Illinois (Median AQI: 41.30)
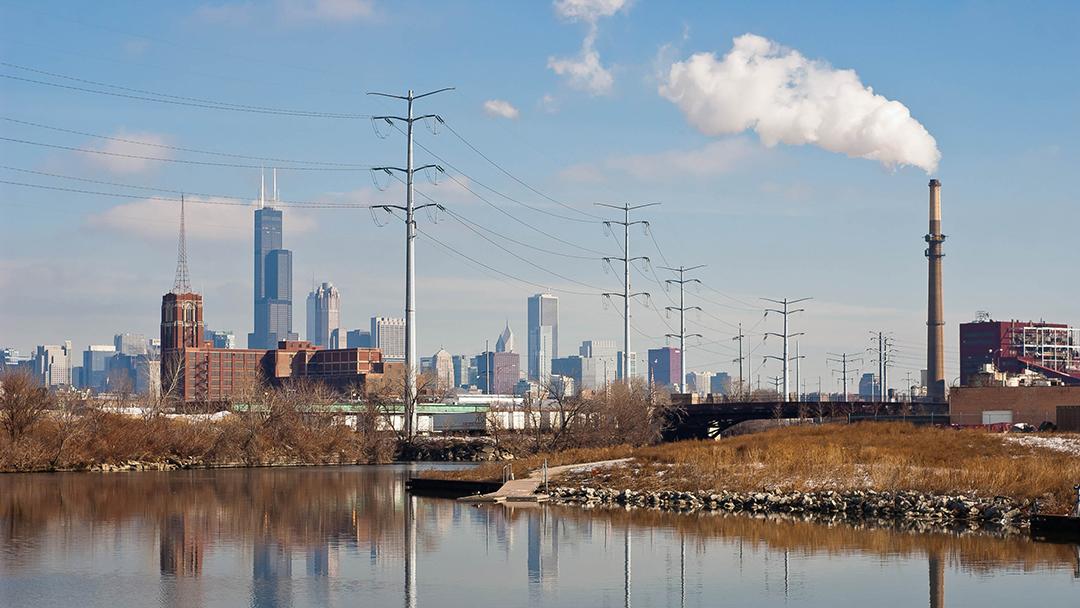

Image Source: WTTW / 2013, Jeremy Atherton
Illinois faces significant challenges concerning ozone and particulate matter pollution. According to the American Lung Association’s 2022 State of the Air report, six counties, including Cook, Lake and Madison County, exhibited unhealthy levels of ozone pollution, also known as smog. Chicago also ranked 16th among the most-polluted cities nationwide for ozone and 22nd for annual particle pollution.
Ground-level ozone arises from emissions emitted by vehicles, power plants and various industrial sources. These emissions react with sunlight, forming ozone. Drought, warm weather and stagnant air contribute to higher ozone levels, especially during summer.
Make it a habit to check the air quality index (AQI) before planning your day. Understand the colors on the AQI scale and what they mean to adjust your outdoor activities accordingly and reduce ozone exposure.
Learn about ozone formation, health risks and the best air purifiers to reduce exposure indoors in our guide to ozone.
#5. Oklahoma (Median AQI: 40.35)

Image Source: KFOR
Like in Illinois, Oklahoma’s primary air pollutants are ozone and particulate matter. The American Lung Association’s 2022 State of the Air report showed increased levels of both contaminants, especially in Oklahoma City.
Oklahoma City’s industrial nature, including chemical manufacturing and power generation, affects the air quality. However, vehicle emissions are the primary source of ozone and particulate matter. The rising temperatures resulting from climate change only increase ozone formation, making it even harder to tackle and clean up. That is why the “ozone season” typically coincides with the warmer months.
Oklahoma’s Air Quality Division offers real-time alerts via email or SMS to stay on top of air pollution levels and protect yourself from exposure to hazardous conditions. You can subscribe here.
Here are our top-pick air purifiers for traffic pollution to improve indoor air quality during days with high ozone and particulate matter levels.
Hot, fast-growing cities in the sun belt have the worst air quality
All 20 cities with the worst air quality are in the Sun Belt states of Arizona, California, New Mexico and Texas. Hot, fast-growing cities in this region combine factors that make air pollution particularly bad. Phoenix, for example, gets more sun than nearly any city. Sunlight and heat can worsen air pollution, triggering chemical reactions between oxygen and pollutants like car exhaust to create ozone.

Add to the mix increasing emissions from rapid urbanization — Phoenix has more than doubled its population over the last 30 years — and it is easy to see why these fast-developing cities in the Southwest create a vicious cycle for air pollution.
Meanwhile, the cities with the best air quality are in cooler, slower-growing regions with plentiful vegetation and green space. Of the 20 cities with the best air quality, four are in Virginia, and three are in Colorado, while Alaska, Montana and Texas are each home to two.
How to deal with poor air quality
When the air quality is poor, avoiding spending time outdoors and minimizing exposure is advisable. But outdoor pollutants can find their way into your home, especially during days or in areas with high levels of air pollution. Maintaining good indoor air quality is as essential as reducing outdoor activities.
You can improve indoor air quality with the following tips:
1. Vacuum regularly
Regular vacuuming is essential to prevent dust and particulate matter from accumulating in your home. Opt for a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter to capture particles and prevent them from re-entering the air. Also, remember to change the filter regularly.
2. Avoid using wood-burning stoves and heaters
When wood burns, it releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs), oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and other fine particulates (PM2.5) that can contribute to indoor pollution. During periods of high outdoor pollution, ventilation is not recommended, and these pollutants can easily linger indoors.
3. Consider investing in an air purifier
HEPA air purifiers are highly effective in removing particulate matter, dust and other pollutants from the air.
| 👑 BEST OVERALL | 💰 FOR TIGHT BUDGETS | 🛋️ FOR LARGE SPACES | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Levoit Core 600S | Levoit Core 300 | Alen Breathsmart 75i | |
 |  |  | |
| AIR CLEANING SPEED ⚡ | 15 minutes | 40 minutes | 24 minutes |
| CADR 👩🔬 | 410 CFM (697 m³/h) | 145 CFM (246 m3/h) | 347 CFM (589 m³/h) |
| FILTER TECHNOLOGY 💨 | H13 True HEPA filter and integrated activated charcoal filter | H13 (Medical) Grade HEPA and Activated Charcoal | True HEPA H13 filters with activated carbon pellets + Ionizer technology |
| MAX ROOM SIZE 📏 | 635 ft² | 219 ft² | up to 1,300 sq. ft. |
| WEIGHT ⚖️ | 13.7 lbs (6.2 kg) | 7.5 lbs (3.4 kg) | 27 lbs (12.2 kg) |
| OUR REVIEW 🔍 | Levoit Core 600S review | Levoit Core 300 review | Alen 75i review |
| PRICE 💵 | $299.99 | $99.99 | Price not available |
Last update on 2025-07-03 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
4. Ventilate your home when the air is cleaner
Check the daily air pollution forecasts at airnow.gov to know the air quality in your area. If the forecast is good, make sure to open windows to let fresh air in.
Final thoughts
Air pollution is a product of both natural and man-made causes. But while certain geographical and climate factors like desert heat and sun predispose some parts of the country to air pollution, most harmful emissions are created by people.
The improvement in U.S. air quality since 1970 has been one of the most significant public health achievements of the last 50 years. Still, progress is uneven and much of the country — as many as 1 in 3 Americans — live in places with unhealthy levels of air pollution.
And as concerns over COVID-19 continue to highlight the urgency of respiratory health, knowing where and why air pollution in the United States becomes more important than ever.
SOURCES
- American Lung Association. (2023). “State of the Air” 2023 Key Findings. lung.org
- Correia et. al. (2014). The Effect of Air Pollution Control on Life Expectancy in the United States: An Analysis of 545 US counties for the period 2000 to 2007. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- National Weather Service. (2023). Why Air Quality Is Important. weather.gov
- The Canadian Lung Association. (2023). Breathe. lung.ca
- The Historical Market Database (2023). U.S. County Seat List. hmdb.org
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2023). Air Quality – Cities and Counties. epa.gov




