You’ve undoubtedly landed on this page because you have a critical question on your lips… What exactly does an air purifier do? You may have even seen one in a friend’s house, in your child’s classroom, in a waiting room, on the news or in a store and thought, “Do I need one of those?”
Studies by the EPA show how running an air purifier in your home will drastically increase air quality. In simple terms, an air purifier cleans the air by removing harmful airborne pollutants.
Danny explains it nicely in the video below:
Now we know the fundamentals, let’s look further into how an air purifier cleans the air.
Understanding how air purifiers work
Air purifiers comprise two essential components: a fan and a filter. The fan draws in air, passing it through one or a series of filter(s), then pushes the air back into the room. The filters trap particles and gasses, removing them from the air.
It’s as simple as that.
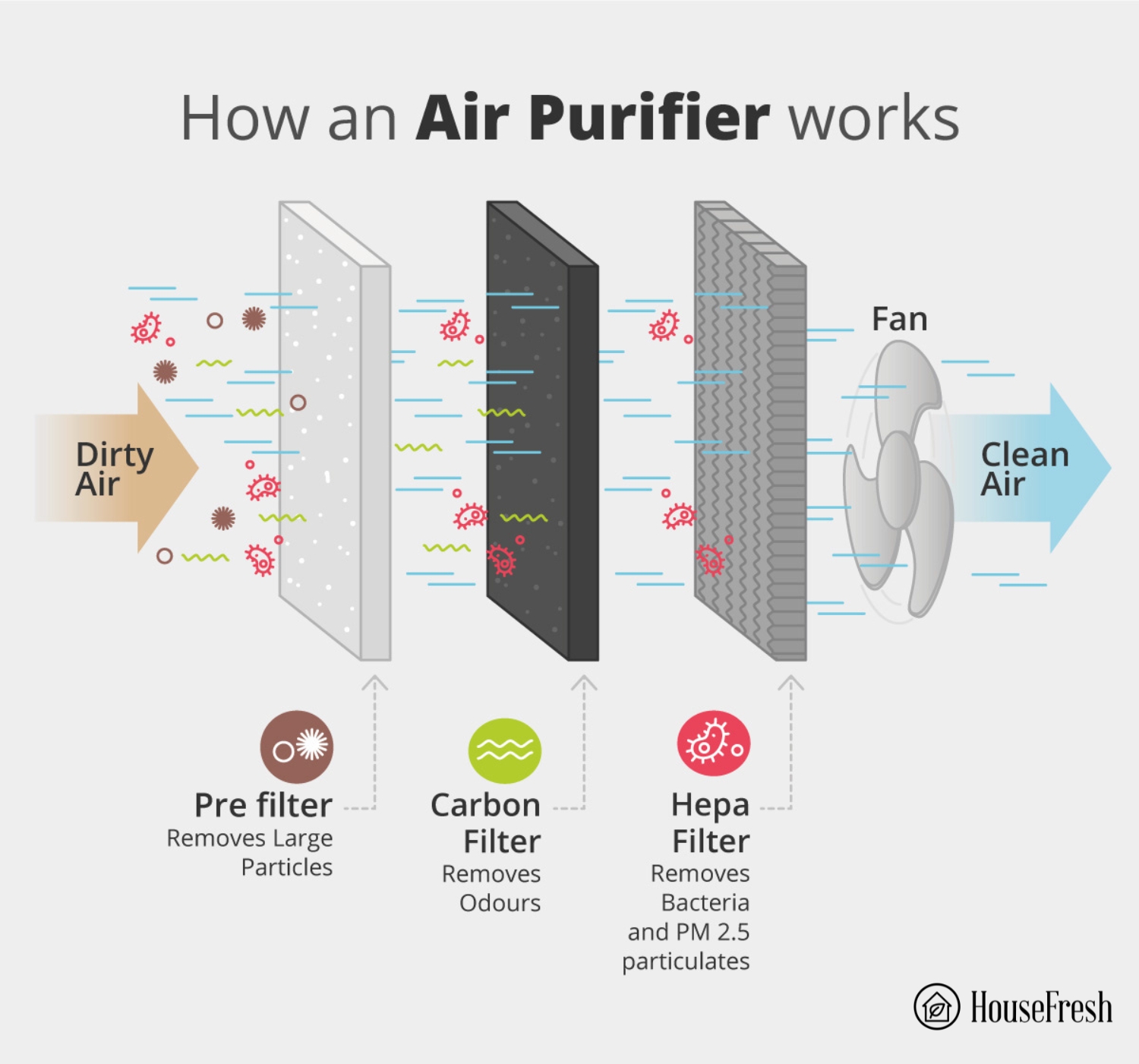
The filters found most commonly in air purifiers are engineered to remove microscopic particles from your air, with the strength and type of filter being determined by the size of the particles it can trap.
Modern air purifiers commonly utilize a combination of air filters, including a pre-filter, a main particle filter and an activated carbon filter. Let’s look at each component more closely.
- Pre-filter: The pre-filter works like a sieve and picks up the large stuff you can see, such as hair or large dust particles – it will help reduce the number of particles that go into the main filters to prolong their life.
- Main particle filter: The main filter is usually made of synthetic materials or fiberglass and does the majority of the air cleaning particles of different sizes:
- Particles measuring up to 10 microns become stuck in the filter fibers as they can’t pass through the holes.
- Particles less than 10 microns down to 0.3 microns could pass through the holes in the filter, but due to Inertial Impaction, these particles can’t change direction as quickly as the airflow, so they bump into the filter medium and get stuck.
- As tiny particles less than 0.03 microns are so small, they constantly bump into air particles. Due to this constant movement, they also keep bumping into the filter material, increasing the chance of being stuck each time as they take a zig zap pattern through the filter. This process is called Brownian Motion, so even non-HEPA-grade filters can block these microscopic particles.
- Activated carbon filter: While particles of all sizes can be blocked with a particle filter, gasses will just pass through, which is why many air purifiers also use activated carbon filters. Activated carbon has many tiny holes that can trap gasses and remove them from the air through a process called Adsorption. Eventually, the carbon will become full, so you need to replace it regularly for it to continue to be effective.
This combination of filters allows air purifiers to capture pet hair, dust, mold spores, pollen, pet dander, mold spores, smoke, viruses, bacteria, odors and chemical gases. What is more, studies have shown that running an air purifier in your home can even prevent transmission of the virus that causes COVID-19.
Pre-filters need to be vacuumed regularly to extend the life of particle and activated carbon filters. Many air purifiers, come with removable and washable pre-filters to make it even easier to stay on top of cleaning them.
The main particle filters need replacing periodically. When these filters trap pollutants, those particles have nowhere to go. This means over time, the filter becomes full and ineffective. You must replace this filter when prompted to keep your air purifier working to its full potential. Most modern air purifiers will have a filter replacement indicator light, which will illuminate when it’s time to change filters.
The carbon in the activated carbon filters will eventually become full with gases and will start to smell bad. That is the sign that you need to replace the carbon filter so it can continue to trap gases and odors.
What types of particles can air purifiers remove from the air?
Air purifiers are the most effective way of removing particles from the air, but there are some things that they can’t do. Let’s look at some of the most prevalent.
Particles air purifiers can remove
Particles air purifiers can’t remove
Other questions you may have about air purifiers
So now you know what an air purifier does and how it can improve the air quality in your home. But you probably have a few more follow-up questions.
No. You will still need ventilation in your home.
Whether that’s opening doors and windows or running an HVAC system, ventilation is key to keeping air circulating throughout your space alongside your air purifier. HVAC systems can even be fitted with pleated filters (the same found in most air purifiers).
A pleated filter could be HEPA grade, but it doesn’t need to be, as lower grade filters can still do a good job of removing pollutants as you can pass the air through the filters multiple times.
Whilst HEPA is required in scenarios like an operating theatre or a nuclear plant as you don’t want any particles to escape, for cleaning the air in the home, a non-HEPA grade filter can handle a higher airflow and will actually clean your room of particles quicker as more air can pass through the filters.
It all depends on the air purifier. Air purifiers are often expensive because they are either high-performance units for larger spaces or use sophisticated technology like AQI sensors and smart functions.
Unfortunately, this isn’t always the case, as some brands have been known to bump up their prices simply because of their brand status. Others make exaggerated claims about their air purifier’s performance to warrant a higher price tag.
Don’t rely on an air purifier’s price; find the right unit that matches your space.
Overall, air purifiers don’t use large amounts of electricity to run. On average, they contribute less than 1% to household energy consumption.
Air purifiers are manufactured to be energy-efficient, but some are more efficient than others. Many units are tested by a third party, Energy Star and given certification to show their efficiency.
- Tip: If you want to know more, check out our guide: How much electricity does an air purifier use?
So… Do you need an air purifier?
Air purifiers are amazing yet simple devices. With only a few components, an air purifier can radically change the air quality in your home.
They are scientifically proven to improve air quality by removing harmful pollutants. All those particles in our air caused by traffic, factories, cigarette and wildfire smoke (the list goes on) make their way into our homes, where we breathe them in.
Introducing an air purifier into your home gives you a better quality of life with clean air. That’s why I strongly recommend that every household has at least one.
But it’s not only pollution particles an air purifier can remove. If you suffer from allergies like pollen, pets, dust or mold, the right unit will trap these allergens in its filters, relieving your symptoms.
Even though air purifiers may seem like an extra expense, they don’t cost much to run, and the benefits far outweigh the cons. You can even make your own air purifier with a box fan, an HVAC filter and some duct tape.
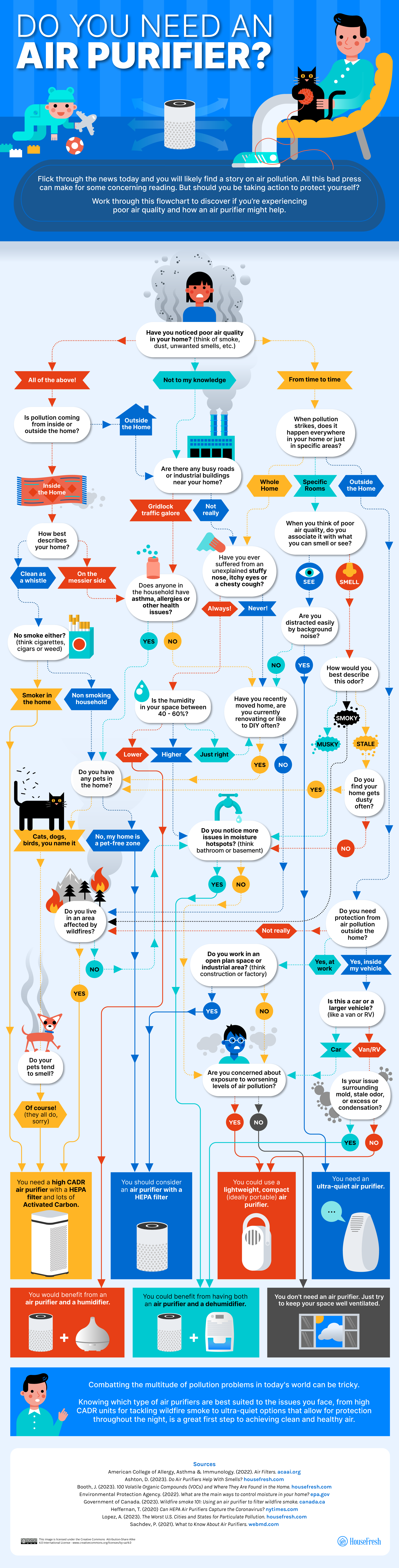
And if you’re still unsure about whether you should get an air purifier or not, give our flowchart a try:
Before I leave you, it is worth mentioning that many air purifiers are tested by the Association of Home Appliance Manufacturers to test the efficacy of air filters in removing dust, pollen and smoke from the air. If you’re in the market for an air purifier, I highly recommend you check out the list of certified units on the AHAM Verifide website, as it is a great way to ensure whatever unit you’re buying has been tested by a third party.
If you have any further questions or comments, just drop us an email and someone from our team will get back to you.
SOURCES
- AHAM Verifide. (2024). Certified Room Air Cleaners. ahamdir.com
- Elfstrom. D. (2024). HEPA should always be the filter of choice. x.com
- Energy Star. (2024). ENERGY STAR Certified Room Air Cleaners. energystar.gov
- National Institutes of Health. (2021). Selection and Use of Portable Air Cleaners. tools.niehs.nih.gov
- Tsang. D. (2023). Can Air Purifiers Remove CO2?. smartairfilters.com
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2018). Guide to Air Cleaners in the Home. epa.gov
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2023). Air Cleaners and Air Filters in the Home. epa.gov
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2023). Air Cleaners, HVAC Filters, and Coronavirus (COVID-19). epa.gov





